Value Converter Wizard
Quickly create a Value Converter and reference it on your XAML code
Introduction
Value Converters extends Xamarin.Forms binding engine by allowing custom logic to run when you need to bind a value from a source in which the type is different from the destiation where it will be consumed. The official documentation provides further information about the feature itself.
To create a Value Converter you need to create a class that implements the IValueConverter interface and then reference it on the Resources Dictionary of the Page or Application that you wish to use it. That's where the Value Converter Wizard comes in, to facilitate this creation and reference, by providing a stub of the converter and let you focus on the conversion logic.
Using the Wizard
The Wizard can be invoked from MFractor Main Menu, under the Wizards sub-menu. Notice that the option will only appear if the loaded solution contains a Xamarin.Forms project.
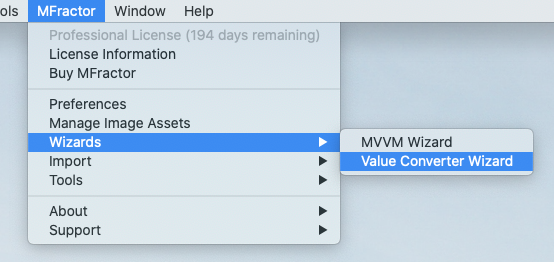
The Wizard Window is divided in two sections: parameters and preview. The parameters control the behaviour of the newly created Value Converter and the options are as follows:
Name and Location Parameters
- Name: Required. The name of the Value Converter, will also be used to name the file that will hold the code. By convention Converters adds a
Convertersuffix to its name. - Infer Input/Output Types: MFractor can infer the input and output data types based on the name you set for the converter. As an example, if you name a converter like
IntToBoolConverterit will infer that the input parameter is of typeintand the output parameter will be abool. Please see the Automatic Type Inference documentation to learn more. - Folder: the folder where the converter will be created inside the project. Defaults to
Converters.
Type Parameters
Optionally you can specify the types for the arguments you can use to process a value converter. The default code snippet for generating a value converter adds type-casting to the chosen types for each argument. Those fields expects a valid .NET/C# data-type
Those parameters are optional and if omitted will default to
object.
Input Type
Represents the type of the input parameter that is the data that is been passed to the converter from the source binding property. As an example, if your View Model declares a string property and it's bound to a property that uses your converter, this value is passed through value argument of the Convert method. In the default code snippet the value argument will be cast to the input local variable on the method.
Output Type
Represents the type of the output parameter, that is the data that will be returned from the converter. This information is used to feed the ValueConversion attribute that is added to your Value Converter on the default Code Snippet. Even though not being used directly in the method body, this information is used by the Analyzers to identify when you used a converter on a property which the type is different from what is expected to be returned.
Parameter Type
Value converters allow passing an additional parameter that can be used for further customize its behavior. Parameters are passed along with the binding declaraction on the property, such as:
<Label Text="{Binding Text,
Converter={StaticResource converterReference},
ConverterParameter='parameter data'}" />
The value parameter data is passed through the parameter argument on the Convert method. In this case the value is a string, but you can also bind to the converter parameter itself.
The Parameter Type field allows you to specify the type of this parameter and it will be made available through the param local variable on the method body cast to this type.
Optional XML Entry
- Create XML Entry: check this option for the wizard to add an entry to the Resource Dictionary of a Page XAML file or App.xaml file to allow access to the newly created Value Converter.
- Add XAML Entry To: select the file to which you want to add the entry of the new Value Converter. Only supported files (.xaml) will be listed here.
If you check this option and select a destination file MFractor will add a declaration for the Value Converter on the ResourceDictionary of that file, such as:
<ResourceDictionary>
<converters:BoolNegationConverter x:Key="boolNegationConverter"/>
</ResourceDictionary>
MFractor will also take care of adding the required namespace imports to the file.
Default Code Snippet
This is the default code snippet of a Value Converter file.
using System;
using System.Globalization;
using Xamarin.Forms;
namespace [DefaultProjectNamespace].Converters
{
[ValueConversion(typeof(object), typeof(object))]
public class $name$ : IValueConverter
{
public object Convert(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
if (value is object == false)
{
return default(object);
}
var input = (object)value;
var param = (object)parameter;
// TODO: Put your value conversion logic here.
return default(object);
}
public object ConvertBack(object value, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture)
{
throw new NotImplementedException();
}
}
}